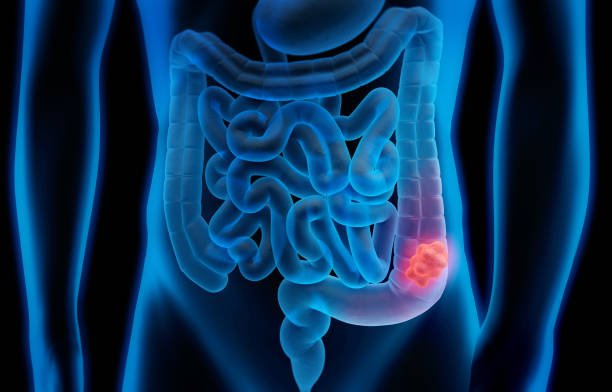
Small bowel cancer is a rare type of cancer that occurs in the small intestine, which plays a vital role in digestion and nutrient absorption. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, nausea, or blood in the stool. Risk factors include Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, genetic conditions, and a high-fat diet. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment, which may include surgery, chemotherapy, or targeted therapy depending on the stage and type of the cancer.
- +91 - 9997385076
- drsurbhigioncosurgeon@gmail.com
- Max Superspeciality hospital, patparganj
- drsurbhigioncosurgeon@gmail.com
- +91- 9997385076