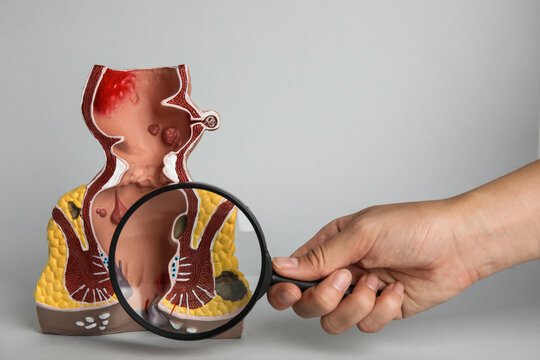
Anal cancer is a rare cancer that forms in the tissues of the anus, the opening at the end of the rectum. It often develops from squamous cells lining the anal canal. Symptoms may include bleeding, pain, or lumps around the anus. Risk factors include HPV infection and smoking. Early diagnosis and treatment, which may involve surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, are important for better outcomes and survival.
- +91 - 9997385076
- drsurbhigioncosurgeon@gmail.com
- Max Superspeciality hospital, patparganj
- drsurbhigioncosurgeon@gmail.com
- +91- 9997385076