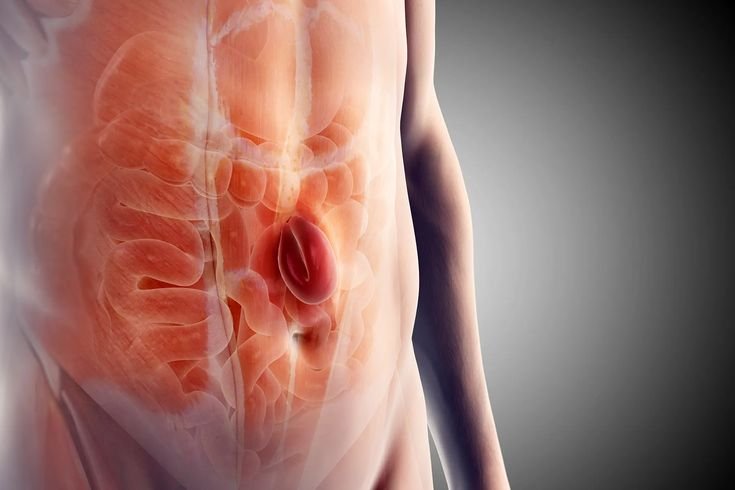
Hiatus hernia occurs when a part of the stomach pushes up through the diaphragm into the chest cavity via the hiatus, an opening for the esophagus. It can cause symptoms like heartburn, acid reflux, and chest discomfort due to stomach acid irritating the esophagus. Hiatus hernias are common, especially in older adults, and are diagnosed through imaging tests like endoscopy or barium swallow. Treatment ranges from lifestyle changes to medications and, in severe cases, surgery.
- +91 - 9997385076
- drsurbhigioncosurgeon@gmail.com
- Max Superspeciality hospital, patparganj
- drsurbhigioncosurgeon@gmail.com
- +91- 9997385076