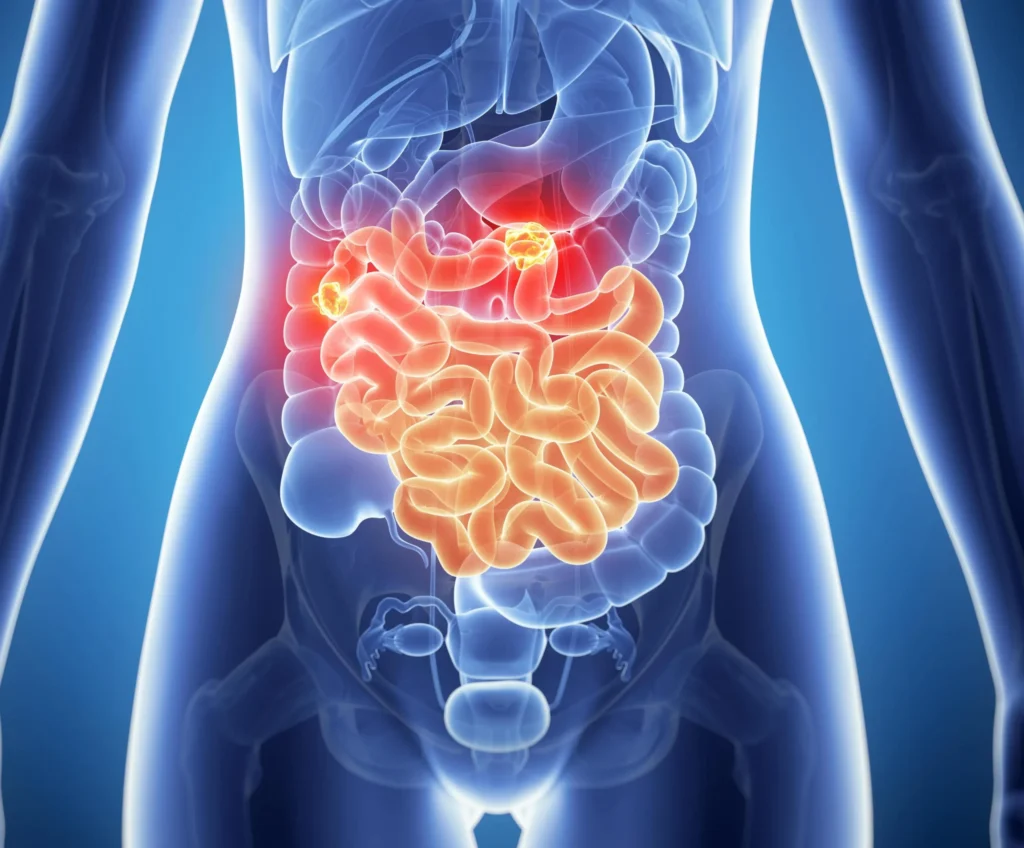
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are rare growths that arise from neuroendocrine cells, which have traits of both nerve and hormone-producing cells. These tumors can develop in various organs, most commonly in the gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, and lungs. NETs may be slow-growing or aggressive and can produce hormones causing distinct symptoms. Early detection and specialized treatment are essential, often involving surgery, medications, or targeted therapies depending on the tumor type and location.
- +91 - 9997385076
- drsurbhigioncosurgeon@gmail.com
- Max Superspeciality hospital, patparganj
- drsurbhigioncosurgeon@gmail.com
- +91- 9997385076